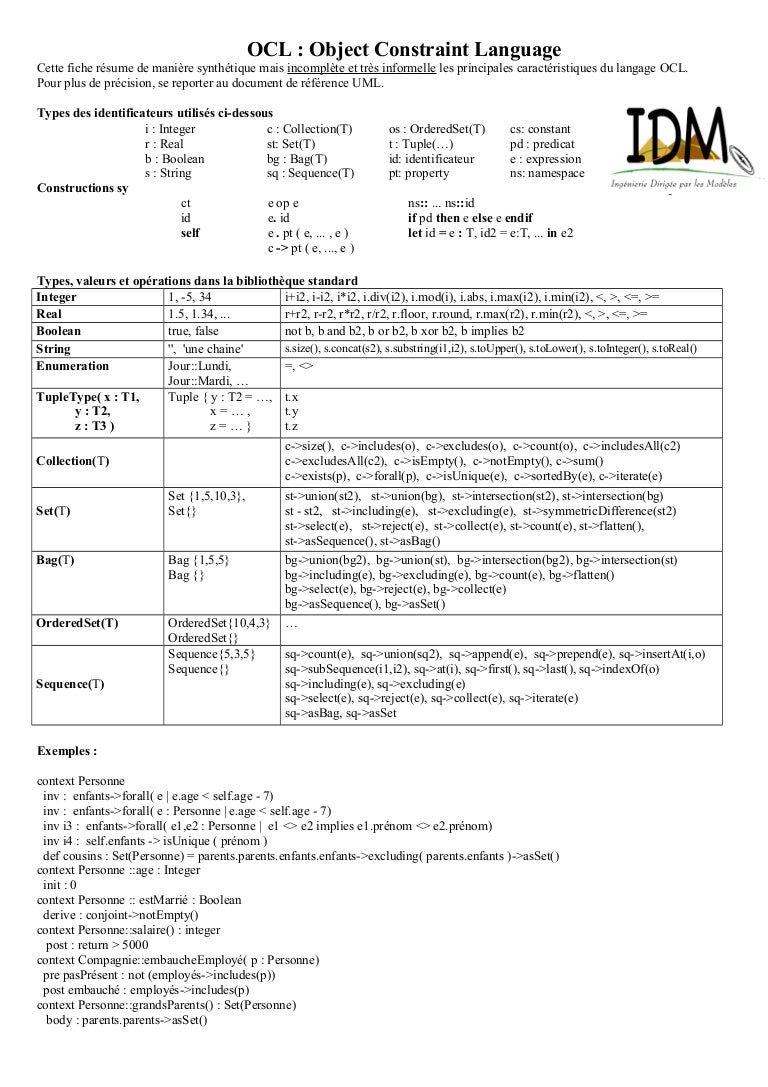
Uml Relationships Cheat Sheet
- Relationship in UML allows one thing to relate with other things inside the system. An association, dependency, generalization, and realization relationships are defined by UML. Composition relationship can also be used to represent that object can be a part of only one composite at a time.
- The class diagram is a very important part of UML.It's a structure diagram and it's purpose is to display classes in the system with all the relationships between them. In my opinion it's the most popular type of diagram in software development.
- Inheritance Relationship Uml
- Uml Cheat Sheet Pdf
- Uml Relationships Cheat Sheet
- Uml Relationships Cheat Sheet Printable
- UML Tutorial
My favourite UML 'cheat sheet' is UML Distilled, by Martin Fowler. It's the only one of his books that I've read that I do recommend. It's the only one of his books that I've read that I do recommend. UML 2 class diagrams are the mainstay of object-oriented analysis and design. UML 2 class diagrams show the classes of the system, their interrelationships (including inheritance, aggregation, and association), and the operations and attributes of the classes.
- UML 2.0 Overview
- UML Useful Resources
- Utilities
- Selected Reading
UML is popular for its diagrammatic notations. We all know that UML is for visualizing, specifying, constructing and documenting the components of software and non-software systems. Hence, visualization is the most important part which needs to be understood and remembered.
UML notations are the most important elements in modeling. Efficient and appropriate use of notations is very important for making a complete and meaningful model. The model is useless, unless its purpose is depicted properly.
Hence, learning notations should be emphasized from the very beginning. Different notations are available for things and relationships. UML diagrams are made using the notations of things and relationships. Extensibility is another important feature whichmakes UML more powerful and flexible.
The chapter describes basic UML notations in detail. This is just an extension to the UML building block section discussed in Chapter Two.
Structural Things
Graphical notations used in structural things are most widely used in UML. These are considered as the nouns of UML models. Following are the list of structural things.
- Classes
- Object
- Interface
- Collaboration
- Use case
- Active classes
- Components
- Nodes
Class Notation
UML class is represented by the following figure. The diagram is divided into four parts.
- The top section is used to name the class.
- The second one is used to show the attributes of the class.
- The third section is used to describe the operations performed by the class.
- The fourth section is optional to show any additional components.
Classes are used to represent objects. Objects can be anything having properties and responsibility.
Object Notation
The object is represented in the same way as the class. The only difference is the name which is underlined as shown in the following figure.
As the object is an actual implementation of a class, which is known as the instance of a class. Hence, it has the same usage as the class.
Interface Notation
Interface is represented by a circle as shown in the following figure. It has a name which is generally written below the circle.
Interface is used to describe the functionality without implementation. Interface is just likea template where you define different functions, not the implementation. When a class implements the interface, it also implements the functionality as per requirement.
Collaboration Notation
Collaboration is represented by a dotted eclipse as shown in the following figure. It has a name written inside the eclipse.
Collaboration represents responsibilities. Generally, responsibilities are in a group.
Use Case Notation
Use case is represented as an eclipse with a name inside it. It may contain additional responsibilities.
Use case is used to capture high level functionalities of a system.
Actor Notation
An actor can be defined as some internal or external entity that interacts with the system.
An actor is used in a use case diagram to describe the internal or external entities.
Initial State Notation
Initial state is defined to show the start of a process. This notation is used in almost all diagrams.
The usage of Initial State Notation is to show the starting point of a process.
Final State Notation
Final state is used to show the end of a process. This notation is also used in almost all diagrams to describe the end.
The usage of Final State Notation is to show the termination point of a process.
Active Class Notation
Active class looks similar to a class with a solid border. Active class is generally used to describe the concurrent behavior of a system.
Active class is used to represent the concurrency in a system.
Component Notation
A component in UML is shown in the following figure with a name inside. Additional elements can be added wherever required.
Component is used to represent any part of a system for which UML diagrams are made.
Node Notation
A node in UML is represented by a square box as shown in the following figure with a name. A node represents the physical component of the system.
Node is used to represent the physical part of a system such as the server, network, etc.
Behavioral Things
Dynamic parts are one of the most important elements in UML. UML has a set of powerfulfeatures to represent the dynamic part of software and non-software systems. These features include interactions and state machines.
Interactions can be of two types −
- Sequential (Represented by sequence diagram)
- Collaborative (Represented by collaboration diagram)
Interaction Notation
Interaction is basically a message exchange between two UML components. The following diagram represents different notations used in an interaction.
Interaction is used to represent the communication among the components of a system.
State Machine Notation
State machine describes the different states of a component in its life cycle. The notations are described in the following diagram.
State machine is used to describe different states of a system component. The state can be active, idle, or any other depending upon the situation.
Grouping Things
Organizing the UML models is one of the most important aspects of the design. In UML, there is only one element available for grouping and that is package.
Package Notation
Package notation is shown in the following figure and is used to wrap the components of a system.
Annotational Things
In any diagram, explanation of different elements and their functionalities are very important. Hence, UML has notes notation to support this requirement.
Note Notation
This notation is shown in the following figure. These notations are used to provide necessary information of a system.
Relationships
A model is not complete unless the relationships between elements are described properly.The Relationship gives a proper meaning to a UML model. Following are the different typesof relationships available in UML.
- Dependency
- Association
- Generalization
- Extensibility
Dependency Notation
Dependency is an important aspect in UML elements. It describes the dependent elements and the direction of dependency.
Dependency is represented by a dotted arrow as shown in the following figure. The arrow head represents the independent element and the other end represents the dependent element.
Dependency is used to represent the dependency between two elements of a system
Association Notation
Association describes how the elements in a UML diagram are associated. In simple words, it describes how many elements are taking part in an interaction.
Association is represented by a dotted line with (without) arrows on both sides. The two ends represent two associated elements as shown in the following figure. The multiplicity is also mentioned at the ends (1, *, etc.) to show how many objects are associated.
Association is used to represent the relationship between two elements of a system.
Generalization Notation
Generalization describes the inheritance relationship of the object-oriented world. It is aparent and child relationship.
Generalization is represented by an arrow with a hollow arrow head as shown in the following figure. One end represents the parent element and the other end represents the child element.
Generalization is used to describe parent-child relationship of two elements of a system.
Extensibility Notation
All the languages (programming or modeling) have some mechanism to extend its capabilities such as syntax, semantics, etc. UML also has the following mechanisms to provide extensibility features.
- Stereotypes (Represents new elements)
- Tagged values (Represents new attributes)
- Constraints (Represents the boundaries)
Extensibility notations are used to enhance the power of the language. It is basically additional elements used to represent some extra behavior of the system. These extra behaviors are not covered by the standard available notations.
“Things” in the Problem Domain
Problem domain = The specific area (or domain) of the users’ business. Scope of the system.Examples: products, sales, shippers, customers, invoices, payments
“Things” eventually modelled.
 Called “classes” (UML) or “entities”
Called “classes” (UML) or “entities”Cardinality symbols ERD relationships
The brainstorming technique
1. Identify a user and a set of use cases.2. Brainstorm with user to ID things involved
3. Use the types of things (categories) to systematically ask questions about potential things, such as the following: Are there any tangible things you store information about? Are there any locations involved? Are there roles played by people that you need to remember?
4. Continue to work with all types of users and stakeholders to expand the brainstorming list.
5. Merge the results, eliminate any duplicates, and compile an initial list.Joint effort between the analyst and the users.
Determine
Determine entities (things in the domain)Attributes (of entities)Keys (Primary, Foreign)Data types (integer, string, etc)Relationships (which entities are related)Cardinality (how are entities related)Details about Entities/Classes
Attribute: describes one piece of information about each instance of the classCustomer has first name, last name, phone number
Identifier or key: One attribute uniquely identifies an instance of the class. Required for data entities, optional for domain classes. Customer ID identifies a customer
Compound attribute: Two or more attributes combined into one structure to simplify the model.
Inheritance Relationship Uml
Object: Class is a type of thing. Object is a specific instance of the class. Each instance has its own values for an attribute
Association (UML) / Relationship (ERD): a naturally occurring relationship between classes (UML term). # rep by Multiplicity/Cardinality. 1 to 1 or 1 to many.
Domain Class Model Diagram with an association
Types of things
Tangiblee.g. book, plane, car, hat, document, worksheetRoleEmployee, Customer, doctorOrg unitDivision, department, teamDevicesSensor, timer, machine, printerSites / locationsWarehouse, branch, store, deskIncident / event / interactionFligh, call, logon, order, paymentTypes of associations
UML notation for multiplicity of associations
The Noun Technique
1. Using the use cases, actors, and other information about the system — including inputs and outputs — identify all nouns (names).2. Using other information from existing systems, current procedures, and current reports or forms, add items or categories of information needed.
3. As this list of nouns builds, you will need to refine it. Ask these questions about each noun to help you decide whether you should include it:
- Ask questions, such as is it important and inside the scope, to see if it should be included.
- Ask questions to see if it really should be excluded, such as is it only a report or an input or is it an attribute.
Uml Cheat Sheet Pdf
- Ask questions to see if it needs further research. In other words that you cannot answer whether it needs to be included or excluded.
4. Create a master list of all nouns identified and then note whether each
one should be included, excluded, or researched further.
5. Review the list with users, stakeholders, and team members and then refine the list of things in the problem domain.
Uml Relationships Cheat Sheet
Mechanical approach to identifying classesUml Relationships Cheat Sheet Printable
